-
Phone Number
-
Email Address
This article explores a guide of ecological cities covering a series of functions and needs that is represented in 12 ecological guidelines that can establish themselves as key points in the construction of the characteristics of sustainable cities in based on a report called «12 GREEN GUIDELINES”.
The document developed by CDBC’s (International Advisory Group for Green and Smart) defines rules or standards for smart urban developmenta all levels.
These ecological indicators are disseminated into three large groups: the urban form, the transport and energy, and the resources they describe in a concisely outlines the bases of the sustainable city … How to design more sustainable cities?
Content menu:
Three important sections divide the document with the following guidelines :
Although the reference report is divided by each ecological guideline in: A rationale, explanation of the economic, environmental and social networks, a brief case study and a list of the best practices implemented.
Due to the size of the report, we are interested in focusing on the justification of the possible norms ecological regulations established for cities sustainable and its objectives.
Each city must establish a growth limit urban (UGB = Urban Growth Boundary). He limit should be established on the basis of an analysis rigorous test of sensitivities ecological conditions , the capacity of the environment, and the efficiency or productivity of the various uses of the land. A more compact development, i.e. cities compact , has some direct benefits as as we can see in the image:
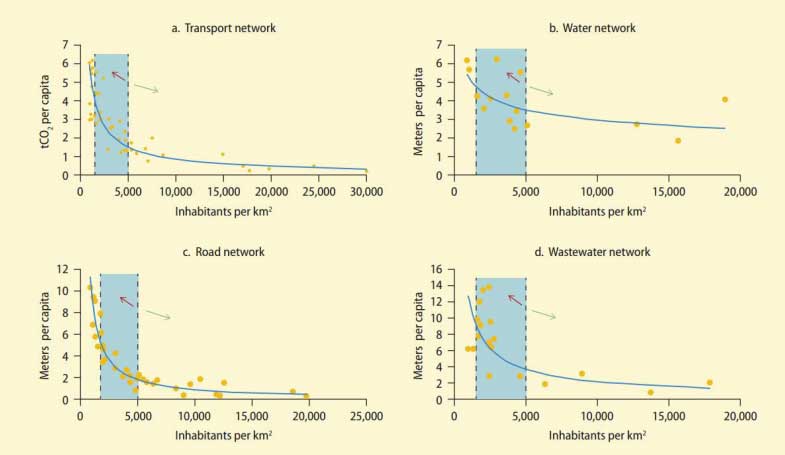
Impact of urban density on the carbon emissions, and the length of water pipes or roads (Source: World Bank).
They are a tool to achieve the compact development of the sustainable city , which helps create conditions conducive to shorter trips and greater efficiency in transport (Increases the efficiency of the public infrastructure in all its aspects), in walking or ride a bike. In addition to protecting the land agriculture, disorderly development and reduces the air pollution.

Graph from The New Climate Economy on Atlanta and Barcelona, similar population but different levels of carbon emissions. This strategy can also increase the value of the built environment with rising costs of housing that can be offset by the decrease in transportation costs. (See also landscapes where the urban growth of 10 is compared cities)
A basic ecological guideline is addresses the growth that maximizes transportation benefits public, while strongly emphasizing its users, people. Public transportation should be the preferred mode of transportation for long-distance travel and short.
The increase in the density of people who work and live around transport stations is one of the the best ways to do public transport more effective, so rules must be established concrete and easy access points to public transport.
To understand more and go into more detail, we already carried out a specific article from City Dot where it was attempted Describe all the points of interest and more
According to the ecological guide , all residential units should be close to at least six types of services within the radius of 500 meters from the entrance of the residential building (Services: schools, post offices, banks, rental, clinics, activity centers, restaurants, etc).
The relationship between workers and residents (The number of workers divided by the number of residents) must be between 0.5 and 0.7. Configured within a spatial area that should not be be more than 15 km2 to improve the city sustainable .
The blocks must be less than or equal to 2 hectares and 70% of the blocks must comply with this standard. Exceptions for areas industrial. The small blocks are the essential element of efficient networked urban transport. They create a dense mesh of narrow streets and paths that they are more pedestrian friendly.
They create a variety of public spaces, architectures and activities, adding to the vibrancy of the neighborhood. With “superblocks” , all traffic is concentrated in some main avenues. The net result, it's traffic congestion.
Wide streets also create obstacles to movement pedestrians, thus favoring drivers more. designing sustainable metropolises !
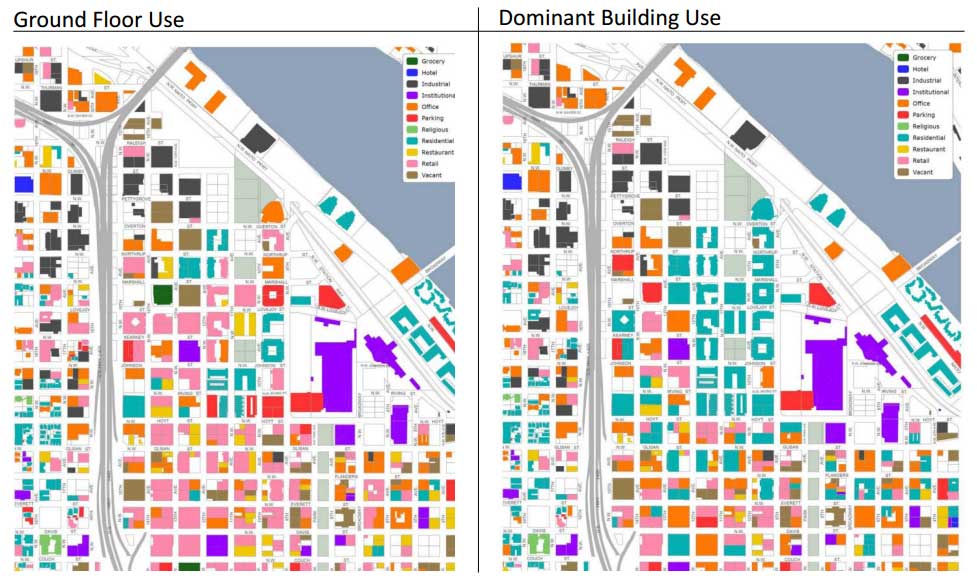
These two charts show the success of using small blocks combined with mixed use in the city.
Publicly, according to indicators green accessible and usable green space must comprise between 20-40% of the urban area built (Residential areas must have a larger coverage). All residences must have a accessible public space less than 500 meters away.
Within urbanism , large spaces public spaces allow a diverse group of people to live together together, they create economic vitality and an increase of the value of the properties.
Public spaces can give identity to neighborhoods and a sense of place, which is vital to the building community and improving the quality of life. High levels of density can make areas urban ecological such as awkward or tight spaces.
There should be connected areas for pedestrians of at least 10 km in length for every square kilometer urban , without architectural barriers. The routes of cyclists at least 10 km long per kilometer square in urban areas.
The ecological orientation established in the most attractive cities in the world emphasize the pedestrian environment on a human scale. No pollution occurs, while providing benefits for human health. Dense webs for walking and riding a bike allow children to more efficient commuting, encouraging people from neighborhoods happier and healthier.

A New York study confirms that they increase sales considerably when space is increased in paths for pedestrians and cyclists.
All new urban actions when urbanizing must be within a radius of 500 meters from a bus or public transport station . For the city as a whole, at least 90% of the evolution must be within a radius of 800 meters from a station public transport.
Making public transportation accessible is an option first class, one of the best ways to reduce the car dependency in the area metropolitan . If public transport is an option first class, people often choose not to drive.
Other benefits, among them is the price increase of the house, as can be seen in the following graph:
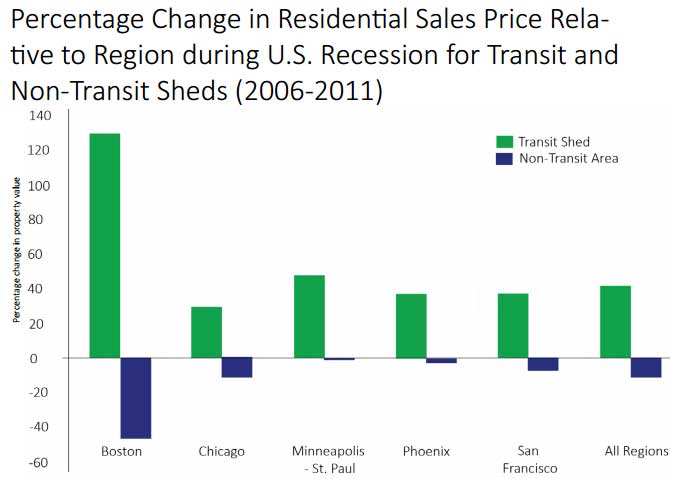
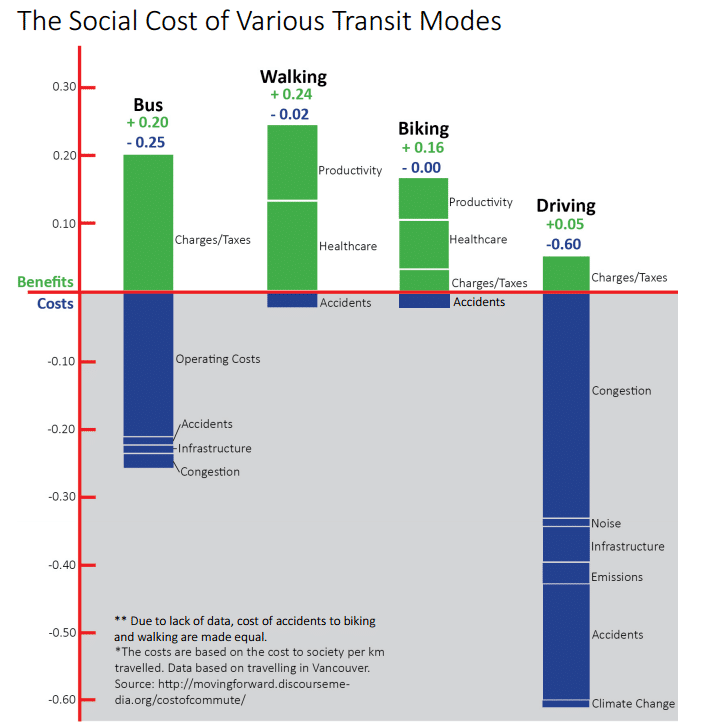
Within the ecological guidelines each The city must have a strategy for the control of the vehicles and their parking, undoubtedly goes coupled with quality public transport. Here plays a fundamental role the economic, environmental cost, of health, clean air…etc.
In the following graph we can see the costs social in variation of the models of transportation :
In the so-called «green architecture« there must be policies and rules organic consistent measures that require a minimum ratio of buildings that contain some standard qualification according to urban profile. (Let us remember the article urban profile that we introduced into energy consumption)
As investors and residents understand the importance of the environmental and social impacts of greener constructions , increase the possibilities before a commercialization of the greener buildings.
See more in the article construction analysis sustainable.
With the application of sustainable and coherent measures in the population reduction of 30 possible to 50 percent in primary energy consumption in a city. Here technology plays a fundamental role and they must measures and economic items to be applied to act with forcefulness in the metropolises of the future .
All buildings should be equipped with waste classification . all waste Domestic must be selected. waste collection dangerous must be a priority. At least 30-50% of the waste should be composted and 35-50% recycled or reused.
The circular economy plays an important role in sustainable cities :

All buildings in cities should have 100% in the adoption of devices of saving water. In the green spaces that surround buildings should adopt plants that require low water consumption .
All drinking water should be controlled and at least 20-30% of the water supply should be recycled from any of the waters sewage and rainwater.

This graph demonstrates that the technologies applied to water efficiency are profitable and therefore we must undertake initiatives that promote this facet for the benefit of everyone.
Reference report “12 GREEN GUIDELINES” developed by CDBC's (International Advisory Group for Green and Smart)… HERE