-
Phone Number
-
Email Address
If we look at human existence, the history of housing have varied drastically throughout of time and centuries; size, materials, height, design, types…etc. From the caves of our ancestors cavemen or houses made of straw and earth with a duration of more than one hundred years, until the first house printed in 3D in its entirety.
To start with, we would like to first release a short film very interesting about “history of house”…
Different techniques and types of construction that enhance the attitude of man in search of shelter and the perfect home . This video represents the evolution of housing to try understand the key points of the history of architecture from home.
A short film created and developed by Jackie Lay and Originally published in The Atlantic. Now we want to try In short, the evolution of housing through the time and by seasons.
Content menu:
The history of housing has been and will be very long, but We have tried to understand what has happened to this day and How has the dwelling and habitat of beings evolved? human.
First, we want to provide a historical chronology from the transformation of construction to the present days with the following scheme:
| Historical timeline and construction evolution | |
| 10,000 BC | Natural materials are used. Wood, clay, adobe bricks for houses and barns. |
| 4800 BC | Megaliths are used in tombs and temples. (Stonehenge, Great Britain) |
| 4200 BC | The Dolmen is used to cover graves near the homes. (Country Clare, Ireland). |
| 3200 BC | Settlements evolve in forms, materials and building systems (Skara Brae. United Kingdom). Culture Sumer in Mesopotamia. Ziggurats are built. Materials: stone, adobe. |
| 3100 BC | Egyptian culture. The pyramids of Giza are built. Materials: stone, adobe, wood. |
| 3000 BC | Tombs and temples reach proportions monumental. (Tomb of Menga. Antequera, Spain). |
| 1800 BC | New materials and tools are used (Age of the Bronze). The houses evolve in their function and distribution |
| 1200 BC | The Olmec culture settles in the Gulf of Mexico. They built the first cities of Mesoamerica. |
| 776 BC | Greek culture. The Acropolis is built. Materials: limestone, marble. |
| 750 BC | Roman culture. The City is founded. is built the Coliseum. Materials: limestone, marble. |
| 312 AD c. | Emperor Constantine orders the construction of Christian churches, architecture emerges Paleochristian. |
| 330 AD | Byzantium is the new capital of Rome, they are built monumental temples, architecture emerges Byzantine |
| 790 AD | The first monasteries are built in Germany, later in Spain. The Romanesque emerges early. |
| 1140 AD | The abbey of Saint Denis is built in France. The “architecture of light” emerges. The Gothic |
| 1420 AD c. | The aesthetic theories of the old are resumed Rome and Vitruvius' book “De Architecture” |
| 1550 AD | The Baroque, an architectural style, arose in Italy loaded with ornamentation, light, color and textures. |
| 1640 AD | Neoclassical architecture. It arose in France after the Baroque. Architecture returned to the classical styles of a monumental way |
| 1750 AD c. | The Industrial Revolution. The steam engine arose serial production. Steel and Concrete are used. |
| 1850 AD | 19th century. Industrial Architecture, Functionalism and Bauhaus, Modern Movement. |
| 1980 AD | Due to the great advances in Technology, the High Tech architecture and architects who are beginning to use computer programs in projects from 1984 – 1985. |
| 2002 AD | BIM development appears in housing projects and buildings that begin to be used from Autocad. The major architecture firms immerse themselves in their possibilities. |
| 2013 AD | Parametric and adaptive architecture appears where the projects, together with the BIM, adapt to the spaces automatically |
As a complement and schematically, the following document chronologically summarizing the different styles architecture and its relationship with art. A guidance document very useful as we can see in the following image:
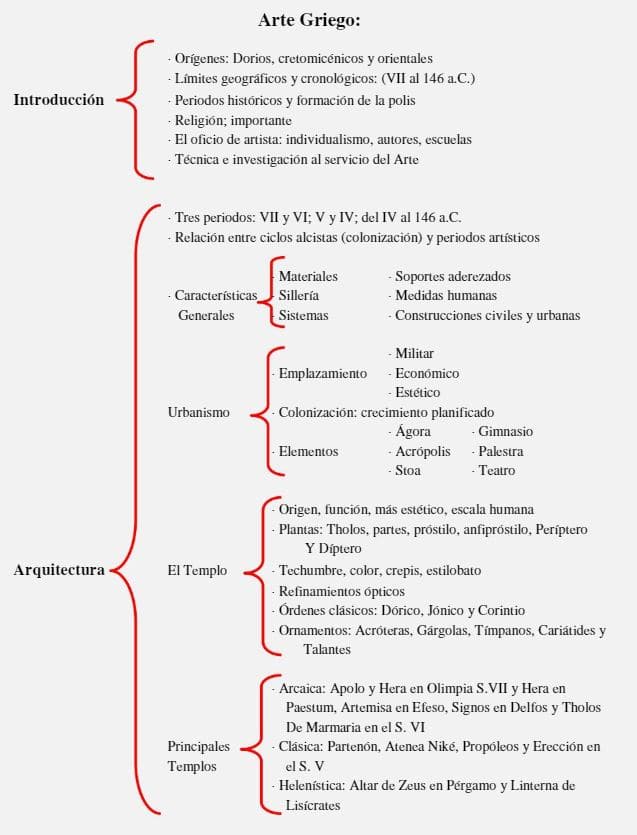
We also recommend this document – which is more visual – and it also inquires into the historical narration of architecture and its relationship with the different artistic styles.
The specific features of a house depend on the time, terrain, free materials, techniques edifying, of the historical moment in its relationship with art and abundant symbolic factors such as social class or the economic resources of their owners.

Houses can be built above or below grade of floor, although most of the modern residences They are located at a higher level than the ground, sometimes on semi-buried cellars, especially in the days cold.
The most used materials are the earth itself, wood, bricks, stone, and increasingly iron and concrete, especially in urban areas. Most are often combined with each other, although the choice depends on the architectural project, according to the tastes of the client of the service and, above all, the cost of the material or the simplicity of its implementation.
One of the primordial peculiarities of the vernacular architecture is the use of materials autochthonous. Among them, the most widespread in warm areas and warm has been the land, which can be used raw for manufacture adobes and tapials, or cooked in the form of bricks. Adobe is made up of mud and straw, held together by building blocks that dry in the sun.

The tapial, more suitable for sandstone lands, is works by tamping the material between 2 boards until building a Wall. Another of the vernacular construction materials and very used is lime, binder for the composition of mortars and one of the waterproof coatings most used by the man.
The evolution of housing provides a second characteristic of residences traditions is its perfect adaptation to the physical environment where they interlock. In this way, in areas where the heat of the summer becomes unbearable, the rooms are arranged in around a courtyard, flanked by arcades that allow the Clean air circulates through each and every one of the rooms. In In cold areas, on the other hand, the houses are concentrated in thick walls to preserve the heat of the sun.
In tribal societies residence is usually consist of a single space, where each and every one of the activities. It is frequently built attached to another neighboring building, and is usually far from the site assembly of the tribe or the sacred space. The way of these cabins is repeated throughout the town, producing sometimes fabulous compositions, in Sudan, those of the people Dogon or those of the shepherds of Zambia.
Most of the huts are built from shapes easy geometric shapes, such as, for example, a circular plan surmounted by a conical roof. The construction materials are always and in all circumstances, the natives. If mud is available, it is used to fill the gaps between the warp of branches, or else they are made adobes or bricks. You can also use stems dry, as in the swampy areas of southern Iraq.
The inhabitants of ancient Egypt lived in low houses built with adobes on a quadrangular plan (Today clay bricks have evolved to the example here). The Excavations carried out show that the houses of the slaves They used to have between 2 and 4 rooms and were clustered on an orthogonal grid, with narrow alleys that They ran among the long lines that made up the district, at the It happened that the residences of the foremen were considerably more comfortable.
In the Near East, residences conformed to the constructive possibilities, where there was mud, the beehive-shaped one-room houses; where I don't know found wood, but rather only stone. up to the decks they were built through bands of this material. by rule In general, these traditions have survived to this day and few changes have undergone the evolution of housing from prehistory to the present day d in its techniques constructive, maintaining in many cases aspects bioclimatic factors necessary for efficient housing.
In Pompeii many domus have been preserved, urban residence or a single-family suburban house that has come down to us as the most representative of traditional culture.
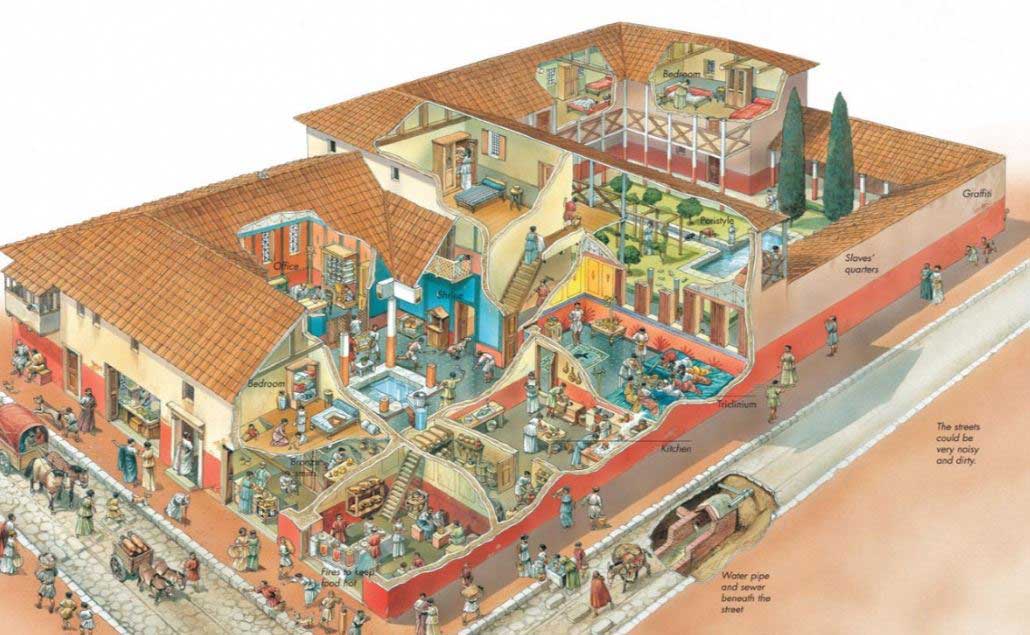
These residences are usually located next to the street that serves as access. After crossing the hall arrives at a semi-covered space called the atrium, a mixture of rooms living room and patio, in the center of which is the impluvium or small pond to collect rainwater.
From the atrium you can access each and every one of the rooms of the house and, on the one hand, to a well-known garden as hortus or peristyle which is surrounded by galleries of columns. At present, many villas continue to maintain the initial traits without differences in the evolution of houses and their distribution.
Insulae were the equivalent of apartment blocks, multi-family residences inhabited by the lower classes humble. The height of these buildings fluctuated between 3 and 5 floors and used to answer complex programs functional. The villas can be understood as houses estates of the most powerful families, and sometimes transformed into genuine residential complexes that occupied multiple hectares between gardens, pavilions and houses. See Art and architecture of the city of Rome.
Each and every one of these residential typologies They disappeared in Europe during the High Middle Ages. coinciding with the demographic crisis of the continent. Yes ok Quite a few people lived under the protection of fiefs and huge castles, many others were crowded into small rooms located in the walls of the small and not so small cities, mainly due to the fact that the countryside was unsafe.

The prosperous farms of old are gone, until the moment when little by little the conditions improved to the shadow of monasteries and urban centers in expansion. A prosperous merchant class then appeared large manor houses began to be built in the cities and rural fiefs. Face the end of the Middle Ages the manor houses they evolved until they became palaces.
These new constructions consisted of complex residences for the ecclesiastical and mercantile nobility, or for the ruling families, who occupied an entire building and contained ritual rooms, chambers for the lords and rooms for a large number of servants and courtiers of all kinds.
The history of housing is complicated and if we look at the palace, even more, was one of the residential typologies that evolved the most throughout the renaissance, becoming into a large-scale urban factor, which has been repeated after On numerous occasions. The first Renaissance palace built in Florence and from there spread to the rest of Europe as the example of the image of London.

In France it was mixed with the medieval castle to produce the château, a rural dwelling that became the center of aristocratic life since the 16th century. Meanwhile, it attempts were made to convert traditional typologies of urban residences by buildings with approximately uniform characteristics, which could be inspired by the models of traditional antiquity.
Objective, to achieve a new baroque city, characterized by the breadth of its perspectives and by the homogeneity of its ends.
The Industrial Revolution produced a huge explosion demographic, fostered by the appearance of a new class society, the proletariat, which lived in overcrowded conditions, in conditions miserable, next to the large industrial centers.
The inconvenience of excessive urban development, associated to the growing interest of the middle classes in having a property residence, gave rise to very different solutions, from the extensions of the old medieval centers to the suburban solutions in the form of a city-garden.
At the end of the 19th century, the residence was among the most essential concerns of architects, and appeared a new science that dealt with planning urban development, alerted by the uncontrolled expansion of the urban centers. Thanks to the new types of transport, the cities grew in 2 directions:
The architecture through the times has evolved in constant movement with a special heyday of residence in petty-bourgeois property (early 20th century) brought with it the survival of historicist styles in construction residential. Up to a certain point, it could be said that the modern typologies have not yet been admitted, especially in single-family works. Already towards the end of the last century a series of architects were projecting residences according to the principles and materials imposed by its season.
Among them stands out the task of Antoni's architecture Gaudí in Catalonia (Spain) where the modernism movement turned the city into a banner of innovation and culture.
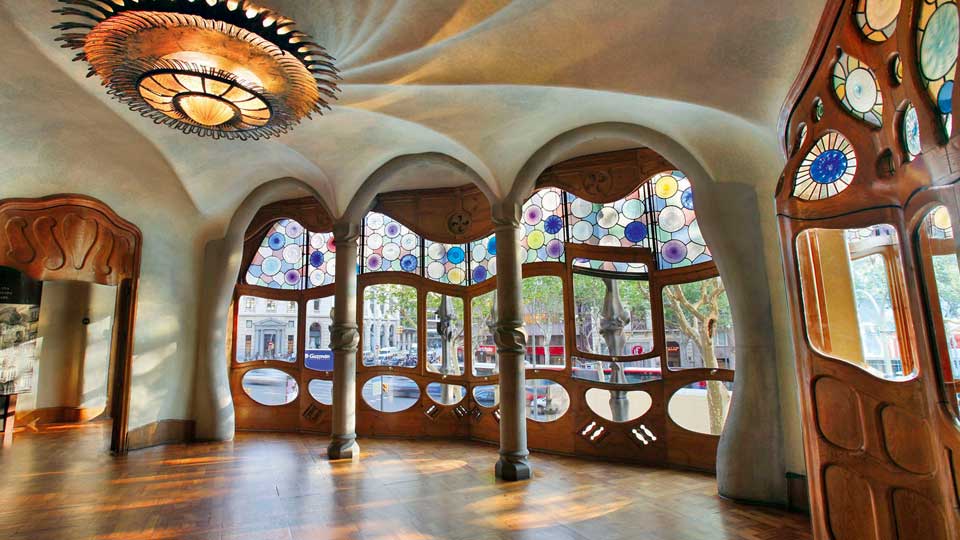

Everyone arrived at certain principles that were later became the seed of modern architecture, such as the open plan to achieve a progressive fluid space, or the possibility offered by the new materials of break the walls through large windows.
After World War I, the residence was transformed into the primary focus of attention for avant-garde architects, and over many years the best built works of the modern movement were residential buildings, such as the house Steiner (1910) by Adolf Loos, the Tugendhat house by Mies van der Rohe, the Schroeder House by Gerrit Rietveld or well the Ville Savoie and the Unité d'Habitation of the great architect Le Corbusier.
Although it is important to acknowledge the history since c
We can highlight the following architectural icons in a summary regarding reference of houses in the 20th century by medium of different illustrated images. A good example of the most perfect architecture!
Mass concrete, the industrialization of precast industrial and housing, the houses made of containers maritime, modular housing, has been during this century the spearhead of an entire architectural revolution.
And in this next video the architects most outstanding and that have revolutionized, in some way, the way in which we currently do things. (Also from a presentation of QUI we can understand a little more)
Houses on the Indian subcontinent change a lot in depending on the area, time and local traditions. In the villas or towns are patio houses and other compact around a single space, while in the highly populated cities abound in flats. The palaces, which found in the most different places, they can be fortified, and those that extend over the terrain They have scattered constructions such as pavilions. The Western repercussion is only perceived in certain areas small and in large urban centers.
In China, the house with a patio and a tiled roof has become preserved over the centuries. It is a walled house, which represents the social order of the traditional extended family. In certain areas there are also strings of residences easier single-family homes, made up of a single room and a small patio or garden. At the opposite extreme are the large palace complexes, such as the Forbidden City from the city of Beijing.
In Japan, the traditional house is concentrated in a progressive quadrangular space, divided by movable panels of rice paper that attempt a convoluted appearance, and flooring through tatamis made of rice straw. The construction is built in wood and covered with tiles if the land has enough space, a complex is added to the little garden. One of the most relevant peculiarities of the Japanese residential architecture is the harmony of proportions and formal simplicity.
Western repercussion has been felt in the country Japan more than in other oriental countries, but, at the same time, many of its architects are among the most noted of the modern movement.
Obviously, in an article it cannot be explained in detail the evolution of architecture throughout history. At this point and for more information we have a excellent search engine.
From the Home Repair Care website we have created a search engine for documents that filter information from Google and that only returns results in PDF, Word, books, etc. To the document browser can be accessed from the following link and so that you have an idea of how it works, we leave the following scheme:
I hope it helps you find more data on evolution of construction and the prehistory of housing.