-
Phone Number
-
Email Address
Any city in the world that lends itself wants to have or sponsor the label of Smart City or city intelligent. A very broad concept with different versions and guidelines.
With technology came innovation and sensors to collecting data. If we apply it to development practices based on sustainability, we managed to improve the asset Management; institutions, public transport and private, companies or the inhabitants of the city.
The concept is broad, but we will go step by step…
Content menu:
The Smart City is defined as a smart city (intelligent city) that combines technology with the analysis of data to improve the services offered by a city , reduce energy costs and the impact environmental.
Obviously, as a definition in itself, it is not new, since initially before the appearance of this idea, let's call it “Cool” , there were sustainable cities, livable cities, healthy cities, cities safe, bioclimatic cities, cities green…etc . The only thing, that now, we have the technological capacity to process more information to improve the services.
A series of qualifiers, which have become the Smart Cities (In English) or commonly called smart cities ( Intelligent cities ).
As we see in the previous image, the intense use of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT ) is an important part of these city smart who wants to change the world thanks to knowledge of the data and information .
Although we can understand what is a Smart City , it is important to emphasize why they appear. Here comes into play that half of the world's population lives in cities with the forecast managed by the United Nations that indicates that 70% of human beings will live in urban centers in 2050.
This body… “Warns that the increase in population of cities can become a real problem, unless harmony can be maintained between the spatial, social and environmental aspects of the localities, as well as as among its inhabitants ” … The influence of these consequences poses a challenge.
In turn, seeing the new digital business opportunities that are presented, the big information companies, computing and electronics, take advantage of such a social situation to get a new consumer market. He sponsors the “Smart City” … Where technology in the city exerts an important factor.
Population trends in the megacities of the future …

So, taken together, I could say they represent a new urban development whose objective is to improve the cities towards sustainability through information digital extracted from the sectors and layers that form the city. Here, knowledge of information play a crucial role!
It is curious, that the main cities labeled as "Smart City" are reciprocated and protected by the big companies like Telefónica, IBM or Microsoft…etc. But this is another topic for discussion.
In collaboration with Barcelona, Buenos Aires and others major cities around the world , Boyd developed a set of indicators to support the assessment Comparison of smart cities . The cities digital media can be identified (or categorized) in six dimensions.
The smart cities Wheel ( Smart Cities) is a holistic framework for consider the key components that make a city be smart.
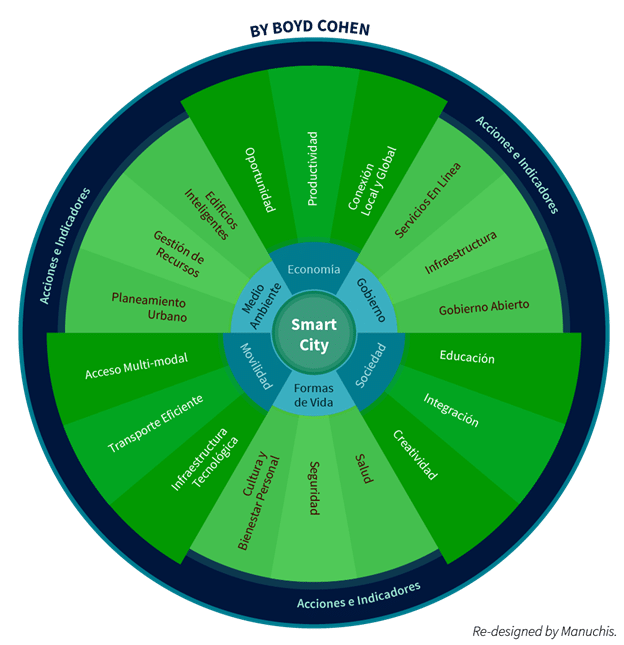
These six axes or dimensions connect with the theories of development and urban growth. And, to be more specific, are based -respectively- on theories of regional competitiveness, economics of transport and ICT, natural resources, social and human capital, quality of life and citizen participation in the governance of cities.
The automatic and efficient administration of urban infrastructures, will range from the possibility of create new services that better respond to the needs specific to each city, up to the possibility of identify future problems that may come to confront the urban space.
There are a number of factors to complement in the extension of every city whose deficiencies must be supported and aided by other resources while determining future problems and be able to act "before they happen".
This ideal or idealized model of a city that needs a digital transformation in an environment technologically appropriate, it encompasses a series of subcategories:
It consists of the smart city having generation distributed throughout the territory: the supply is personalized, micro-generation, not centralized.
Implementation of electric vehicles in cities and others motor elements, such as motorcycles, and the respective positions public and private charging stations.
Citizens and inhabitants are undoubtedly the most essential, since without their active participation it is not possible to be able to do these ideas.
The smart grids are known as Smart Grids interconnected, those that have circulation in both directions of data between the Service Center or center of control and the user who inhabits the city.
As a model of effectiveness and efficiency, buildings have to be smarter and more energy efficient. Buildings with home automation and other electronic elements that respect the environment and have systems of integrated energy production.
It is about the intelligent measurement of spending data of each user, by means of telemeters where readings are made remotely and in real time.
The smart sensors are going to have the function of compiling each and every one of the precise data to make the city smarter. They are an essential part of sustain connectivity and also information, and make that each subsystem fulfills its function.
Smart cities collect data using The technologies of the information and communication (ICT) . Information bases that are analyzed by very complex data analysis programs that provide information summaries.
As an example of a model of the Smart-City and how the data is collected by the smart cities . We can see the complexity that can be reached in a small municipality in the following image:
A city can be classified as a digital (or smart) when you invest in human and social capital, in traditional infrastructures (transport) and modern (ICT), in infrastructure of fuel communications, in
As we can see in the infographic on the cover of this article, there must exist and coexist a symbiosis in four benchmarks to provide a solid foundation; Human Aspect, Government, Environment and Economy that will imply a commitment of the different agents involved in an improvement process constantly in order to improve the quality of life, both of the environment and its inhabitants, so the advantages Smart City are:

Although it should be noted that each city is different and according to administrations have led the implementation in a direction or another, if we can highlight some achievements main ones like:
Not all that glitters is gold, and in the world of technological cities there are a number of drawbacks closely associated with the technological aspect that can setbacks in the expansion of the city. The smart problems cities are:
Obviously both the advantages and disadvantages are of the appreciation that I have been able to observe and that surely they can enumerate many more in both cases, what I do perceive is that Smart Cities sell us as the need for the future and I no longer know if it convinces me that know how many times I pass by the corner of street "X" or what My house has more "Electronic Cachibaches" than the store electronics in my neighborhood, as examples, everything for… “Being more efficient” or for improving the environment environment and the natural environment, in theory, in about complex ecosystems for the habitat of users.
Although it may not seem like it, as an example from Spain , there is a wide variety of smart cities that are implemented different improvement projects in this sense (Here to see them all in Spain and here in Europe). One of the cities most recognized both nationally and internationally is the city of Santander Smart City .
Part of the blame lies with the approximately 12,000 fixed sensors and as many mobile ones over recent years in strategic locations of the Santander street: buildings, lampposts, litter bins, converted municipal cars and buses now in a kind of information laboratories throughout the city.
We can see from Open Data Santander from here where there are also a wide variety of apps that facilitate data to users.
With all the sensors, local authorities are achieving an example of a smart city in conditions to discover and be informed of a multitude of variables, in real time; the precise location of your fleet of buses, the humidity conditions of each corner of the city, the traffic situation, the pollution indices or the noise level of the municipality.
That is, they can make decisions in a more smart and manage each and every resource involved in the day after day of the city, public and individuals, in a more cost-effective manner and of environmental impact. (Interesting analysis of the implementation of the smart-city concept from here in the city)
London is the smartest city in the world by 2020 , according to the seventh report of the IESE Cities Index in Motion 2020. New York ranks second, followed by from the great city of Paris.
The annual index analyzes the level of development of 174 cities of the world through nine dimensions considered key to truly smart cities and sustainable. These are: the economy, the environment, the human capital, governance, international projection, the transport and mobility, social cohesion, technology and the urban planning of the city.
Links and documents of interest to expand info:
Other articles of interest:
If you liked the article, rate it and share!