-
Phone Number
-
Email Address
The cheaper and lower cost of the solar energy installations in recent years has made renewable energy more accessible than ever, giving rise to an exponential increase in its use from a perspective not only industrial, but also in homes at the worldwide.
So, start thinking about recycling your solar panels is important for all photovoltaic systems provide energy solutions renewable and do not represent a waste load for the future generations. Because… What do we do with the used solar panels?
Solar power is having its heyday absolute. Since the early 2000s, the number of panels solar installed around the world has grown exponentially, and is expected to continue to do so for decades.
At the end of 2020, a estimated amount of 744.6 Gigawatts of solar energy (Reference report published in 2021 HERE)
According to a recent report by the International Agency for Renewable Energies, that figure could reach 4,500 GW in 2050.
But, the solar panels that generate that energy are not they will last forever. The industry standard shelf life is about 25 to 30 years old , which means that some of the panels installed in those beginnings, do not take long to be withdrawn (See report HERE about estimated useful life solar panels ).
And with each passing year, more and more will be removed from the service, glass and metal photovoltaic modules that soon they will start to add up to millions, and then tens of millions of metric tons of material.
This is a subject of vital importance for a successful growth of environmental sustainability and to For this reason, recently the WEEE directive (waste electrical equipment electrical and electronic) has been updated by the EU to greening the life cycle of solar panels.
But… What numbers are we talking about when we intend to recycle medium photovoltaic installations world?
From a report issued by the International Agency for Renewable Energy (IRENA) has already given us They give some brushstrokes of the great work that the recycle thousands and thousands of solar panels.
Countries with more ambitious targets are expected to on renewable energy will provide a greater amount of waste globally. And the rough estimate for 2050 on the volumes of waste accumulated in panels photovoltaics is from:
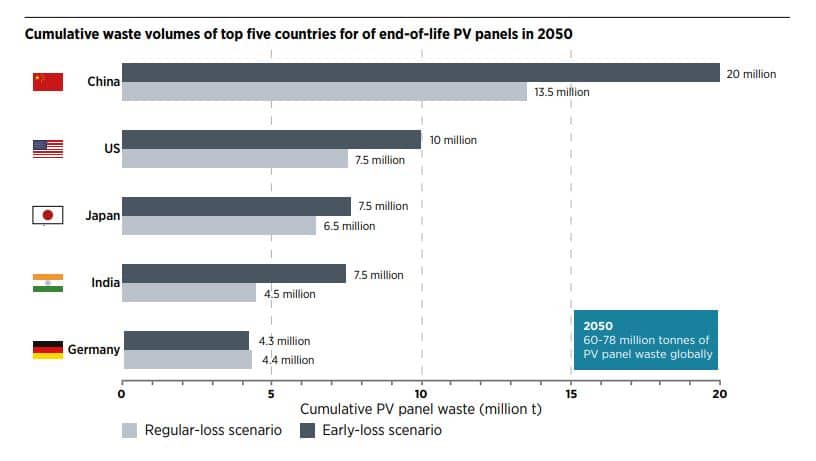
So by 2050 we will have roughly between 60 – 78 million tons of waste in panels photovoltaics all over the world . No kidding!
Currently, only the European Union has adopted specific regulations in the field of recycling . The most countries around the world classify them as garbage or industrial material.
In exceptional cases, how Japan or the United States arrange of general regulations that affect the photovoltaic solar sector and its panels for hazardous material content, and the processes of treatment or destruction of the same, but through a very poor and generalist legislation.
What's more, when talking about the guarantee of use and the parts of a photovoltaic solar panel, nothing is mentioned about the recycled from solar panels .
In the following graph we have the evolution to 2030 of the materials used by different panel technologies such as the percentage of the total mass of the panel:
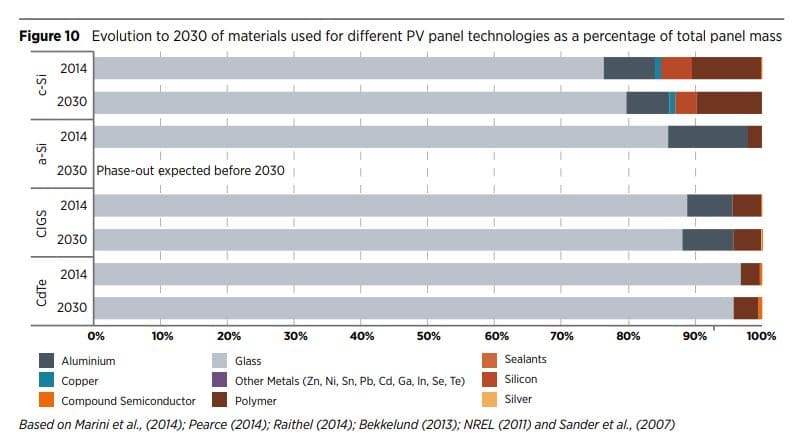
From a value point of view in relation to the materials used, although thanks to technical advances and to new technologies, the use of silver is reducing considerably, silver is by far the most expensive component per unit mass in a panel, followed by the copper, silicon, aluminum, glass and polymers.
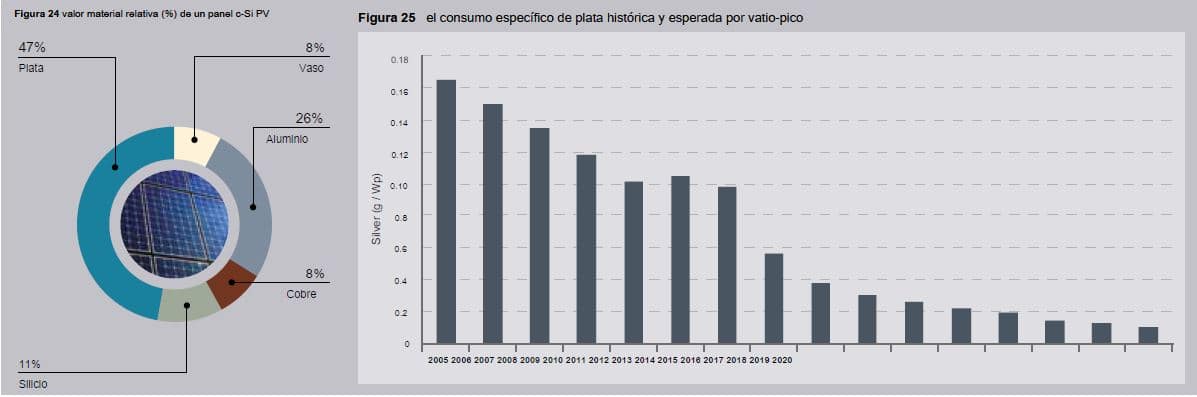
Until now, two different methods of recycling, thermal and mechanical, to ensure the procedure correct in retrieve and put back in cycle production all the materials from which the solar panels. The application of the first or second depends on the presence of silicon in the panel modules solar.
In addition, they are made of many materials, some hazardous, and assembled with adhesives and sealants that difficult to separate, and in many cases, without instructions clear for your recycling process.
We can also see the recycling process in a plant pilot of the Japanese program NEDO:
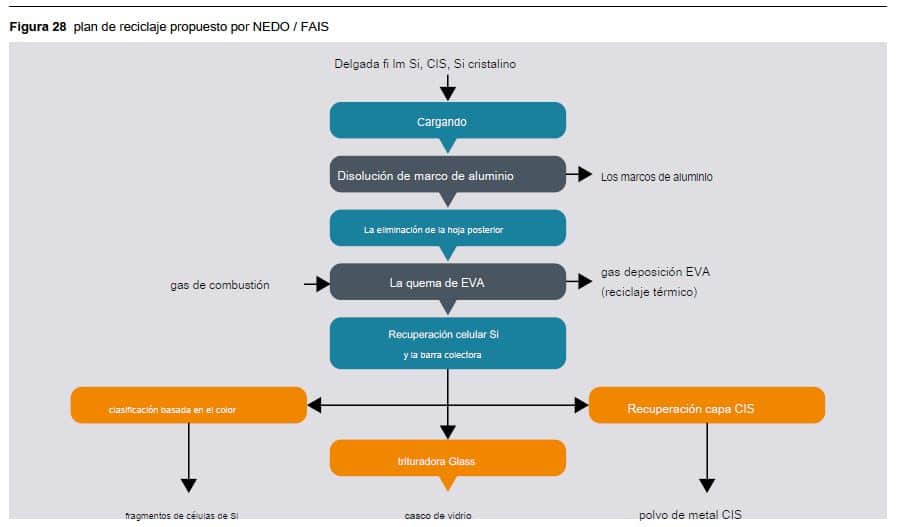
It is estimated that up to 90% of glass and material semiconductor can be reused in new panels or other glass products, but we have to think that almost the 75% of the material that separates is glass, which is easy to recycle into new products but also has a value of resale very low, so the lower the value that a "recycler" can extract, the less incentive to recycle .
According to the Solar Energy Industries Association (Solar Energy Industries Association – SEIA)… “The industry solar is creating programs to train companies businesses that are dedicated to recycling in understanding what contain the manufacturers' products and how break them down, but undoubtedly there is still a long way to go ahead.”
Although there is still a long way to go from the legislative perspective , the objectives of the companies in the long term, will be to make sure that the processes are cheap and efficient enough to deal with the wave of dismantled panels that we are leaving to find around the world. In reality, the cost total has to be so low that no one has to think of another option other than recycling .
And remember that we have an interesting article on what what if you live in a city that only uses energy renewable…